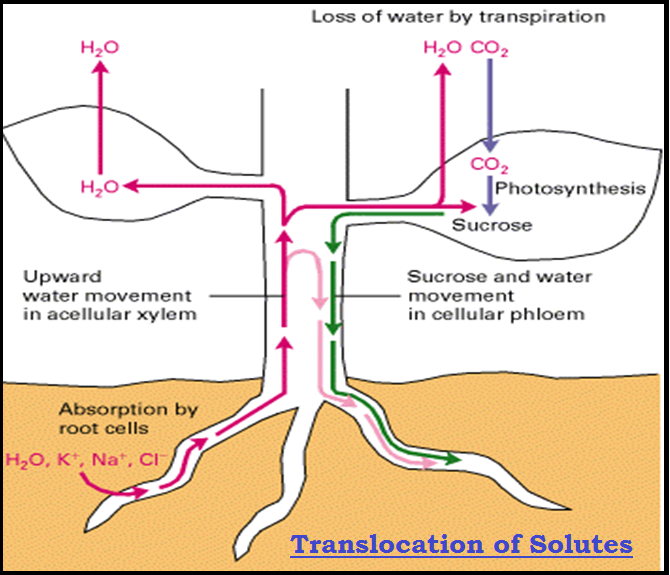
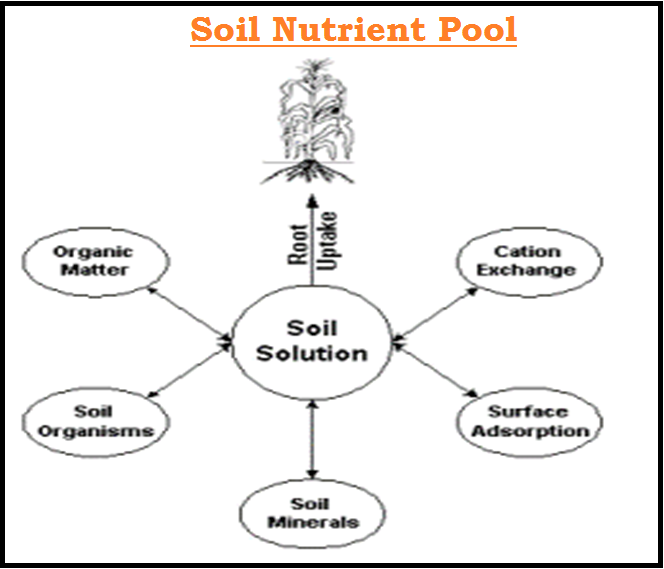
MECHANISM OF ABSORPTION OF ELEMENTS
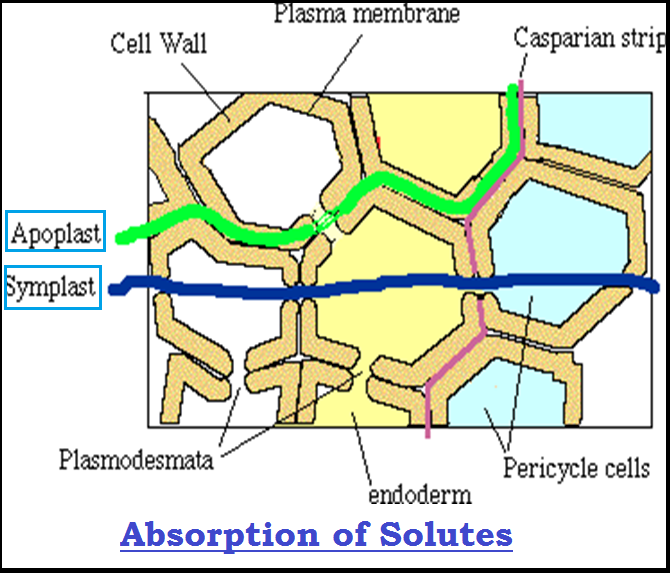
● Much of the studies on `color{violet}"mechanism of absorption"` of elements by plants has been carried out in `color{violet}"isolated cells, tissues or organs"`.
● These studies revealed that the `color{violet}"process of absorption"` can be demarcated into `color{Brown}"two main phases."`
● In the `color{violet}"first phase"`, an initial `color{violet}"rapid uptake of ions"` into the ‘free space’ or ‘outer space’ of cells – the `color{Brown}"apoplast"`, is `color{violet}"passive"`.
● In the `color{violet}"second phase"` of uptake, the ions are `color{violet}"taken in slowly"` into the ‘inner space’ – the `color{Brown}"symplast"` of the cells.
● The `color{violet}"passive movement"` of ions into the `color{violet}"apoplast"` usually occurs through `color{Brown}"ion-channels"`, the trans-membrane proteins that function as `color{violet}"selective pores"`.
● On the other hand, the `color{violet}"entry or exit of ions"` to and from the `color{violet}"symplast"` requires the expenditure of `color{Brown}"metabolic energy"`, which is an process.
● The `color{violet}"movement of ions"` is usually called the inward movement into the cells is `color{Brown}"influx"` and the outward movement, `color{Brown}"efflux"`.
● These studies revealed that the `color{violet}"process of absorption"` can be demarcated into `color{Brown}"two main phases."`
● In the `color{violet}"first phase"`, an initial `color{violet}"rapid uptake of ions"` into the ‘free space’ or ‘outer space’ of cells – the `color{Brown}"apoplast"`, is `color{violet}"passive"`.
● In the `color{violet}"second phase"` of uptake, the ions are `color{violet}"taken in slowly"` into the ‘inner space’ – the `color{Brown}"symplast"` of the cells.
● The `color{violet}"passive movement"` of ions into the `color{violet}"apoplast"` usually occurs through `color{Brown}"ion-channels"`, the trans-membrane proteins that function as `color{violet}"selective pores"`.
● On the other hand, the `color{violet}"entry or exit of ions"` to and from the `color{violet}"symplast"` requires the expenditure of `color{Brown}"metabolic energy"`, which is an process.
● The `color{violet}"movement of ions"` is usually called the inward movement into the cells is `color{Brown}"influx"` and the outward movement, `color{Brown}"efflux"`.